116 KiB
| title | description |
|---|---|
| Documentation | General documentation about how to using SpaceVim, including the quick start guide and FAQs. |
Home >> Documentation
- Core Pillars
- Highlighted features
- Screenshots
- Concepts
- Who can benefit from this?
- Update and Rollback
- Custom Configuration
- Interface elements
- General usage
- Native functions
- Command line mode key bindings
- Mappings guide
- Editing
- Window manager
- Buffers and Files
- Available layers
- Fuzzy finder
- With an external tool
- Custom searching tool
- Useful key bindings
- Searching in current file
- Searching in buffer directory
- Searching in all loaded buffers
- Searching in an arbitrary directory
- Searching in a project
- Background searching in a project
- Searching the web
- Searching on the fly
- Persistent highlighting
- Getting help
- Unimpaired bindings
- Jumping, Joining and Splitting
- Other key bindings
- Advanced usage
- Achievements
Core Pillars
Four core pillars: Mnemonic, Discoverable, Consistent and “Crowd-Configured”.
If any of these core pillars is violated open an issue and we’ll try our best to fix it.
Mnemonic
Key bindings are organized using mnemonic prefixes, like b for buffer, p for project, s for search, h for help, etc…
Discoverable
Innovative real-time display of available key bindings. Simple query system to quickly find available layers, packages, and more.
Consistent
Similar functionalities have the same key bindings everywhere thanks to a clearly defined set of conventions. Documentation is mandatory for any layer that ships with SpaceVim.
Crowd-Configured
Community-driven configuration provides curated packages tuned by power users and bugs are fixed quickly.
Highlighted features
- Great documentation: access documentation in SpaceVim with
:h SpaceVim. - Minimalistic and nice graphical UI: you'll love the awesome UI and its useful features.
- Keep your fingers on the home row: for quicker editing with support for QWERTY and BEPO layouts.
- Mnemonic key bindings: commands have mnemonic prefixes like
[WIN]for all the window and buffer commands or[Unite]for the unite work flow commands. - Fast boot time: Lazy-load 90% of plugins with [dein.vim]
- Lower the risk of RSI: by heavily using the space bar instead of modifiers.
- Batteries included: discover hundreds of ready-to-use packages nicely organised in configuration layers following a set of conventions.
- Neovim centric: Dark powered mode of SpaceVim
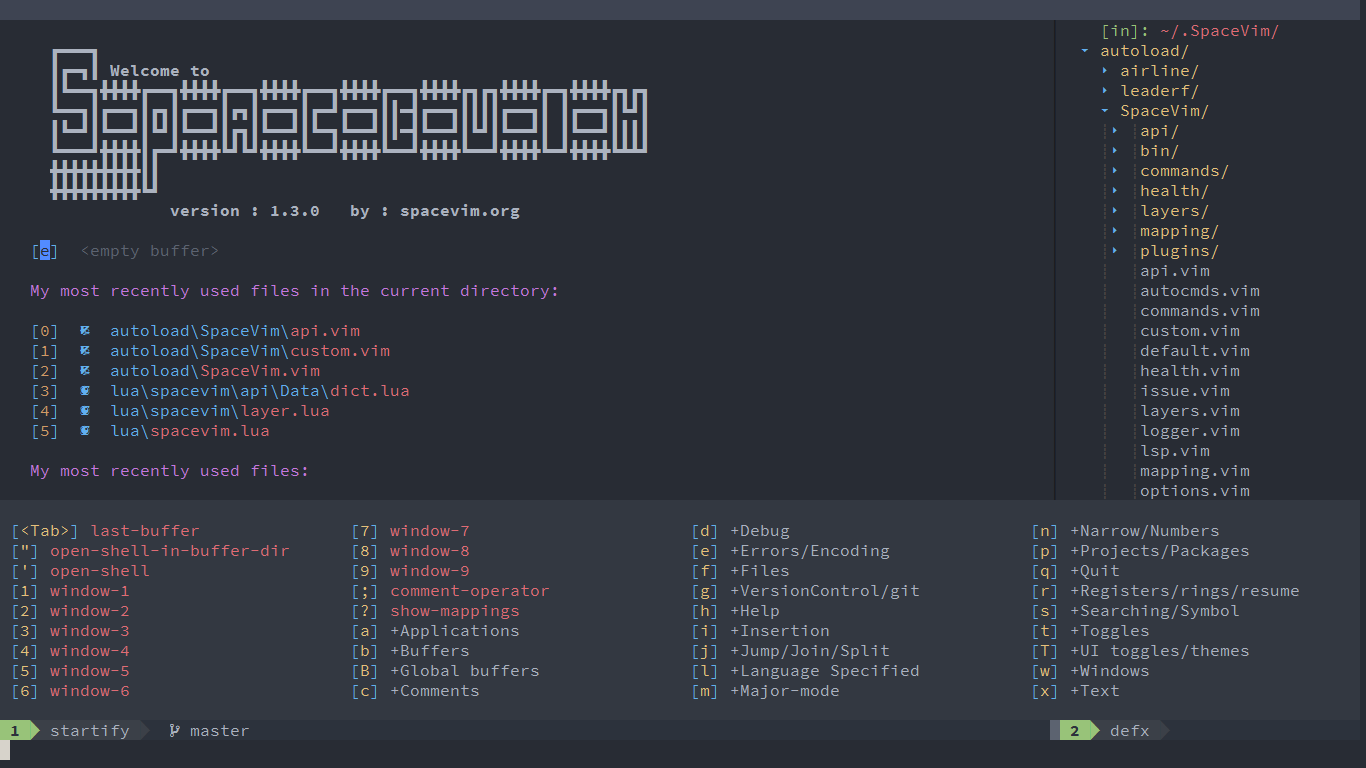
Screenshots
welcome page
working flow
Neovim on iTerm2 using the SpaceVim color scheme base16-solarized-dark
Depicts a common frontend development scenario with JavaScript (jQuery), SASS, and PHP buffers.
Non-code buffers show a Neovim terminal, a TagBar window, a Vimfiler window and a TernJS definition window.
To get more screenshots, see: issue #415
Concepts
Transient-states
SpaceVim defines a wide variety of transient states (temporary overlay maps) where it makes sense. This prevents one from doing repetitive and tedious presses on the SPC key.
When a transient state is active, a documentation is displayed in the transient state buffer. Additional information may as well be displayed in it.
Move Text Transient State:
Who can benefit from this?
- Elementary Vim users.
- Vim users pursuing a beautiful appearance.
- Vim users wanting to lower the risk of RSI.
- Vim users wanting to learn a different way to edit files.
- Vim users wanting a simple but deep configuration system.
Update and Rollback
Update SpaceVim itself
There are several methods of updating the core files of SpaceVim. It is recommended to update the packages first; see the next section.
Automatic Updates
By default, this feature is disabled. It would slow down the startup of Vim/Neovim. If you like this feature, add following to your custom configuration file.
[options]
automatic_update = true
SpaceVim will automatically check for a new version every startup. You have to restart Vim after updating.
Updating from the SpaceVim Buffer
Users can use command :SPUpdate SpaceVim to update SpaceVim.
This command will open a new buffer to show the process of updating.
Updating Manually with git
For users who prefer to use command line, they can use following command in terminal to update SpaceVim manually:
git -C ~/.SpaceVim pull
Update plugins
Use :SPUpdate command to update all the plugins and
SpaceVim itself. After :SPUpdate, you can assign
plugins need to be updated. Use Tab to complete
plugin names after :SPUpdate.
Reinstall plugins
When a plugin is failed to update or is broken, Use :SPReinstall
command to reinstall this plugin.
Get SpaceVim log
The runtime log of SpaceVim can be got via key binding SPC h L.
To get the debug information about current SpaceVim environment,
Use the command :SPDebugInfo!. This command will open a new buffer,
the default information will be shown in this new buffer.
You also can use SPC h I to open a buffer with the
issue template.
Custom Configuration
The very first time SpaceVim starts up, it will ask you to
choose a mode,
basic mode
or dark powered mode.
then it will create a SpaceVim.d/init.toml in your
HOME directory. All the configuration files can be stored in
~/.SpaceVim.d/ directory.
~/.SpaceVim.d/ will be added to &runtimepath.
It is also possible to override the location of ~/.SpaceVim.d/
using the environment variable SPACEVIMDIR. Of course you can
also use symlinks to change the location of this directory.
SpaceVim also support local config file for project, the init
file is .SpaceVim.d/init.toml in the root of your project.
.SpaceVim.d/ also will be added into &runtimepath.
All SpaceVim options can be found in :h SpaceVim-options,
the key is same as the option name with the prefix g:spacevim_
being removed.
Comprehensive documentation is available in :h SpaceVim.
Users can also use SPC h SPC to fuzzy find the documentation
of SpaceVim options. This key binding requires one fuzzy finder
layer to be loaded.
Add custom plugins
If you want to add plugins from github, just add the repo name
to the custom_plugins section:
[[custom_plugins]]
repo = "lilydjwg/colorizer"
on_cmd = ["ColorHighlight", "ColorToggle"]
merged = false
You can also use the url of the repository, for example:
[[custom_plugins]]
repo = "https://gitlab.com/code-stats/code-stats-vim.git"
merged = false
on_cmd option means this plugin will be loaded only when the following commands are called.
merged option is used for merging plugins directory. When merged is true, all files in
this custom plugin will be merged into ~/.cache/vimfiles/.cache/init.vim/ for neovim or
~/.cache/vimfiles/.cache/vimrc/ for vim.
For more options see :h dein-options.
disable existing plugins
If you want to disable plugins which are added by SpaceVim,
you can use SpaceVim disabled_plugins options:
[options]
# NOTE: the value should be a list, and each item is the name of the plugin.
disabled_plugins = ["clighter", "clighter8"]
Bootstrap Functions
SpaceVim provides two kinds of bootstrap functions
for custom configurations and key bindings,
namely bootstrap_before and bootstrap_after.
To enable them you need to add following into
~/.SpaceVim.d/init.toml.
[options]
bootstrap_before = 'myspacevim#before'
bootstrap_after = 'myspacevim#after'
The difference is that the bootstrap_before function will be called before SpaceVim core,
and the bootstrap_after function is called on autocmd VimEnter.
The bootstrap functions should be placed to the autoload directory
in ~/.SpaceVim.d/. In our case, create file ~/.SpaceVim.d/autoload/myspacevim.vim
with contents for example
function! myspacevim#before() abort
let g:neomake_c_enabled_makers = ['clang']
nnoremap jk <Esc>
endfunction
function! myspacevim#after() abort
iunmap jk
endfunction
The bootstrap_before will be called after custom configuration file is loaded.
And the bootstrap_after will be called after Vim Enter autocmd.
If you want to add custom SPC prefix key bindings, you can add them to
bootstrap function, be sure the key bindings are not used in SpaceVim.
function! myspacevim#before() abort
call SpaceVim#custom#SPCGroupName(['G'], '+TestGroup')
call SpaceVim#custom#SPC('nore', ['G', 't'], 'echom 1', 'echomessage 1', 1)
endfunction
Similarly, if you want to add custom key bindings prefixed by language leader key,
which is typically ,, you can add them to the boostrap function. Be sure that the
key bindings are not used by SpaceVim.
function! myspacevim#before() abort
call SpaceVim#custom#LangSPCGroupName('python', ['G'], '+TestGroup')
call SpaceVim#custom#LangSPC('python', 'nore', ['G', 't'], 'echom 1', 'echomessage 1', 1)
endfunction
Vim compatible mode
The different key bindings between SpaceVim and origin vim are shown as below.
-
The
skey does replace cursor char, but in SpaceVim it is theWindowkey bindings specific leader in Normal mode. This leader change be changed viawindows_leaderoption which usesas default variable. If you still prefer the origin function ofs, you can use an empty string to disable this feature.[options] windows_leader = '' -
The
,key does repeat lastf,F,tandTin vim, but in SpaceVim it is the language specified Leader key. To disable this feature, set the optionenable_language_specific_leadertofalse.[options] enable_language_specific_leader = false -
The
qkey does recording, but in SpaceVim it is used to close current window. The option for setting key binding to close current window iswindows_smartclose, and the default valuable isq. If you prefer to use the origin function ofq, you can use an empty string to disable this feature.[options] windows_smartclose = '' -
The
jkkey has been mapped to<Esc>in insert mode. To disable this key binding, setescape_key_bindingto empty string.[options] escape_key_binding = '' -
The
Ctrl-abinding on the command line can auto-complete variable names, but in SpaceVim it moves to the cursor to the beginning of the command line. -
The
Ctrl-bbinding on the command line is mapped to<Left>, which will move cursor to the left. -
The
Ctrl-fbinding on the command line is mapped to<Right>, which will move cursor to the right.
SpaceVim provides a vimcompatible mode, in vimcompatible mode, all the differences above will disappear.
You can enable the vimcompatible mode via adding vimcompatible = true to [options] section.
If you want to disable any differences above, use the relevant options. For example, in order to disable language specific leader, you may add the following lines to your configuration file:
[options]
enable_language_specific_leader = false
Send a PR to add the differences you found in this section.
Private Layers
This section is an overview of layers. A more extensive introduction to writing configuration layers can be found in SpaceVim's layers page (recommended reading!).
Purpose
Layers help collect related packages together to provide features. For example, the lang#python layer provides auto-completion, syntax checking, and REPL support for python files. This approach helps keep configuration organized and reduces overhead for users by keeping them from having to think about what packages to install. To install all the python features users only need to add the lang#python layer to their custom configuration file.
Structure
In SpaceVim, a layer is a single file. In a layer, for example, autocomplete layer, the file is autoload/SpaceVim/layers/autocomplete.vim, and there are three public functions:
SpaceVim#layers#autocomplete#plugins(): return a list of plugins used in this pluginsSpaceVim#layers#autocomplete#config(): layer config, such as key bindings and autocmdsSpaceVim#layers#autocomplete#set_variable(): function for setting layer optionsSpaceVim#layers#autocomplete#get_options(): return a list of all available layer options
Debug upstream plugins
If you found one of the built-in plugins has bugs, and you want to debug that plugin. You can follow these steps:
- Disable this plugin Take disabling neomake.vim for instance:
[options]
disabled_plugins = ["neomake.vim"]
- Add a forked plugin or add a local plugin Use toml file to add custom forked plugins:
[[custom_plugins]]
repo = "wsdjeg/neomake.vim"
# note: you need to disable merged feature
merged = false
Use the bootstrap_before function to add local plugin:
function! myspacevim#before() abort
set rtp+=~/path/to/your/localplugin
endfunction
Interface elements
SpaceVim has a minimalistic and distraction free UI:
- custom airline with color feedback according to current check status
- custom icon in sign column and error feedbacks for checker.
Colorschemes
The default colorscheme of SpaceVim is gruvbox.
There are two variants of this colorscheme, a dark one and a light one. Some aspects
of these colorscheme can be customized in the custom configuration file, read :h gruvbox.
It is possible to define your default themes in your ~/.SpaceVim.d/init.toml with
the variable colorschemes. For instance, to specify desert:
[options]
colorscheme = "desert"
colorscheme_bg = "dark"
| Mappings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC T n |
switch to next random colorscheme listed in colorscheme layer. |
SPC T s |
select a theme using a unite buffer. |
All the included colorschemes can be found in colorscheme layer.
SpaceVim supports true colors in terminal, and it is disabled by default, to enable this feature, you should make sure your terminal supports true colors. For more information see: Colours in terminal.
If your terminal does not support true colors, you can disable SpaceVim true colors feature in [options] section:
enable_guicolors = false
Font
The default font used by SpaceVim is SourceCodePro Nerd Font Mono. It is recommended to install it on your system if you wish to use it.
To change the default font set the variable guifont in your ~/.SpaceVim.d/init.toml file. By default its value is:
guifont = "SourceCodePro Nerd Font Mono:h11"
If the specified font is not found, the fallback one will be used (depends on your system). Also note that changing this value has no effect if you are running Vim/Neovim in terminal.
UI Toggles
Some UI indicators can be toggled on and off (toggles start with t and T):
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC t 8 |
highlight any character past the 80th column |
SPC t a |
toggle autocomplete (only available with autocomplete_method = deoplete) |
SPC t f |
display the fill column (by default max_column is 120) |
SPC t h h |
toggle highlight of the current line |
SPC t h i |
toggle highlight indentation levels (TODO) |
SPC t h c |
toggle highlight indentation current column |
SPC t h s |
toggle syntax highlighting |
SPC t i |
toggle indentation guide at point |
SPC t n |
toggle line numbers |
SPC t b |
toggle background |
SPC t c |
toggle conceal |
SPC t p |
toggle paste mode |
SPC t t |
open tabs manager |
SPC T ~ |
display ~ in the fringe on empty lines |
SPC T F |
toggle frame fullscreen |
SPC T f |
toggle display of the fringe |
SPC T m |
toggle menu bar |
SPC T t |
toggle tool bar |
Statusline
The core#statusline layer provides a heavily customized powerline with the following capabilities:
- show the window number
- show the current mode
- color code for current state
- show the index of searching result
- toggle syntax checking info
- toggle battery info
- toggle minor mode lighters
- show VCS information (branch, hunk summary) (need
gitandVersionControllayer)
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC [1-9] |
jump to the windows with the specific number |
Reminder of the color codes for the states:
| Mode | Color |
|---|---|
| Normal | Grey |
| Insert | Blue |
| Visual | Orange |
| Replace | Aqua |
All the colors based on the current colorscheme
Some elements can be dynamically toggled:
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC t m b |
toggle the battery status (need to install acpi) |
SPC t m c |
toggle the org task clock (available in org layer)(TODO) |
SPC t m i |
toggle the input method |
SPC t m m |
toggle the minor mode lighters |
SPC t m M |
toggle the major mode |
SPC t m n |
toggle the cat! (If colors layer is declared in your dotfile)(TODO) |
SPC t m p |
toggle the cursor position |
SPC t m t |
toggle the time |
SPC t m d |
toggle the date |
SPC t m T |
toggle the mode line itself |
SPC t m v |
toggle the version control info |
nerd font installation:
By default SpaceVim use nerd-fonts, please read the documentation of nerd fonts.
syntax checking integration:
When syntax checking minor mode is enabled, a new element appears showing the number of errors, warnings.
Search index integration:
Search index shows the number of occurrence when performing a search via / or ?. SpaceVim integrates nicely the search status by displaying it temporarily when n or N are being pressed. See the 20/22 segment on the screenshot below.
Search index is provided by incsearch layer, to enable this layer:
[layers]
name = "incsearch"
Battery status integration:
acpi displays the percentage of total charge of the battery as well as the time remaining to charge or discharge completely the battery.
A color code is used for the battery status:
| Battery State | Color |
|---|---|
| Charging | Green |
| Discharging | Orange |
| Critical | Red |
All the colors are based on the current colorscheme.
Statusline separators:
It is possible to easily customize the statusline separator by setting the statusline_separator variable in your custom configuration file and then redraw the statusline. For instance if you want to set back the separator to the well-known arrow separator add the following snippet to your configuration file:
[options]
statusline_separator = 'arrow'
Here is an exhaustive set of screenshots for all the available separator:
| Separator | Screenshot |
|---|---|
arrow |
 |
curve |
 |
slant |
 |
nil |
 |
fire |
 |
Minor Modes:
The minor mode area can be toggled on and off with SPC t m m.
Unicode symbols are displayed by default. Add statusline_unicode_symbols = false to your custom configuration file, statusline will display ASCII characters instead (may be useful in terminal if you cannot set an appropriate font).
The letters displayed in the statusline correspond to the key bindings used to toggle them.
| Key Bindings | Unicode | ASCII | Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
SPC t 8 |
⑧ | 8 | toggle highlight of characters for long lines |
SPC t f |
ⓕ | f | fill-column-indicator mode |
SPC t s |
ⓢ | s | syntax checking (neomake) |
SPC t S |
Ⓢ | S | enabled in spell checking |
SPC t w |
ⓦ | w | whitespace mode |
colorscheme of statusline:
By default SpaceVim only support colorschemes which has been included in colorscheme layer.
If you want to contribute theme please check the template of a statusline theme.
" the theme colors should be
" [
" \ [ a_guifg, a_guibg, a_ctermfg, a_ctermbg],
" \ [ b_guifg, b_guibg, b_ctermfg, b_ctermbg],
" \ [ c_guifg, c_guibg, c_ctermfg, c_ctermbg],
" \ [ z_guibg, z_ctermbg],
" \ [ i_guifg, i_guibg, i_ctermfg, i_ctermbg],
" \ [ v_guifg, v_guibg, v_ctermfg, v_ctermbg],
" \ [ r_guifg, r_guibg, r_ctermfg, r_ctermbg],
" \ [ ii_guifg, ii_guibg, ii_ctermfg, ii_ctermbg],
" \ [ in_guifg, in_guibg, in_ctermfg, in_ctermbg],
" \ ]
" group_a: window id
" group_b/group_c: stausline sections
" group_z: empty area
" group_i: window id in insert mode
" group_v: window id in visual mode
" group_r: window id in select mode
" group_ii: window id in iedit-insert mode
" group_in: windows id in iedit-normal mode
function! SpaceVim#mapping#guide#theme#gruvbox#palette() abort
return [
\ ['#282828', '#a89984', 246, 235],
\ ['#a89984', '#504945', 239, 246],
\ ['#a89984', '#3c3836', 237, 246],
\ ['#665c54', 241],
\ ['#282828', '#83a598', 235, 109],
\ ['#282828', '#fe8019', 235, 208],
\ ['#282828', '#8ec07c', 235, 108],
\ ['#282828', '#689d6a', 235, 72],
\ ['#282828', '#8f3f71', 235, 132],
\ ]
endfunction
This example is the gruvbox colorscheme, if you want to use same colors when
switching between different colorschemes, you may need to set
custom_color_palette in your custom configuration file. For example:
[options]
custom_color_palette = [
["#282828", "#a89984", 246, 235],
["#a89984", "#504945", 239, 246],
["#a89984", "#3c3836", 237, 246],
["#665c54", 241],
["#282828", "#83a598", 235, 109],
["#282828", "#fe8019", 235, 208],
["#282828", "#8ec07c", 235, 108],
["#282828", "#689d6a", 235, 72],
["#282828", "#8f3f71", 235, 132],
]
Custion section
You can use bootstrap function to add custom section to statusline, for example:
function! s:test_section() abort
return 'ok'
endfunction
call SpaceVim#layers#core#statusline#register_sections('test', function('s:test_section'))
Then, add test section to statusline_right_sections option:
[options]
statusline_right_sections = ['cursorpos', 'percentage', 'test']
Tabline
Buffers will be listed on the tabline if there is only one tab, each item contains
the index, bufname and the filetype icon. If there are more than one tab, all
tabs will be listed on the tabline. Each item can be quickly accessed by using
<Leader> number. Default <Leader> is \.
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
<Leader> 1 |
Jump to index 1 on tabline |
<Leader> 2 |
Jump to index 2 on tabline |
<Leader> 3 |
Jump to index 3 on tabline |
<Leader> 4 |
Jump to index 4 on tabline |
<Leader> 5 |
Jump to index 5 on tabline |
<Leader> 6 |
Jump to index 6 on tabline |
<Leader> 7 |
Jump to index 7 on tabline |
<Leader> 8 |
Jump to index 8 on tabline |
<Leader> 9 |
Jump to index 9 on tabline |
g r |
Switch to alternate tab (switch back and forth) |
Note: SPC Tab is the key binding for switching to alternate buffer.
Read Buffers and Files section for more info.
SpaceVim tabline also supports mouse click, left mouse button will switch to buffer, while middle button will delete the buffer.
NOTE: This feature is only supported in Neovim with has('tablineat').
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
<Mouse-left> |
Jump to the buffer |
<Mouse-middle> |
Delete the buffer |
Tab manager:
You can also use SPC t t to open the tab manager windows.
Key bindings within tab manager windows:
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
o |
Close or expand tab windows. |
r |
Rename the tab under the cursor. |
n |
Create new named tab below the cursor tab |
N |
Create new tab below the cursor tab |
x |
Delete the tab |
Ctrl-Shift-Up |
Move tab backward |
Ctrl-Shift-Down |
Move tab forward |
<Enter> |
Jump to windows under the cursor. |
File tree
SpaceVim uses vimfiler as the default file tree, and the default key binding is <F3>.
And SpaceVim also provides SPC f t and SPC f T to open the file tree.
To change the filemanager plugin:
[options]
# file manager plugins supported in SpaceVim:
# - vimfiler (default)
# - nerdtree
# - defx
filemanager = "defx"
VCS integration is supported, there will be a column status, this feature may make vimfiler slow, so it is not enabled by default.
To enable this feature, add enable_vimfiler_gitstatus = true to your custom configure.
Here is a picture for this feature:
There is also an option to config the direction of file tree, by default it is right. To move the file tree to the left,
you can use filetree_direction option:
[options]
filetree_direction = "left"
File tree navigation
Navigation is centered on the hjkl keys with the hope of providing a fast navigation experience like in vifm:
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
<F3> / SPC f t |
Toggle file explorer |
| with in file tree | |
<Left> / h |
go to parent node and collapse expanded directory |
<Down> / j |
select next file or directory |
<Up> / k |
select previous file or directory |
<Right> / l |
open selected file or expand directory |
N |
Create new file under cursor |
r |
Rename the file under cursor |
d |
Delete the file under cursor |
K |
Create new directory under cursor |
y y |
Copy file full path to system clipboard |
y Y |
Copy file to system clipboard |
P |
Paste file to the position under the cursor |
. |
Toggle visible ignored files |
s v |
Split edit |
s g |
Vertical split edit |
p |
Preview |
i |
Switch to directory history |
v |
Quick look |
g x |
Execute with vimfiler associated |
' |
Toggle mark current line |
V |
Clear all marks |
> |
iecrease filetree screenwidth |
< |
dncrease filetree screenwidth |
<Home> |
Jump to first line |
<End> |
Jump to last line |
Ctrl-Home |
Switch to project root directory |
Ctrl-r |
Redraw |
Open file with file tree.
If only one file buffer is opened, a file is opened in the active window, otherwise we need to use vim-choosewin to select a window to open the file.
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
l / <Enter> |
open file in one window |
s g |
open file in an vertically split window |
s v |
open file in an horizontally split window |
General usage
The following key bindings are the general key bindings for moving cursor.
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
h |
move cursor left |
j |
move cursor down |
k |
move cursor up |
l |
move cursor right |
<Up>, <Down> |
Smart up and down |
H |
move cursor to the top of the screen |
L |
move cursor to the bottom of the screen |
< |
Indent to left and re-select |
> |
Indent to right and re-select |
} |
paragraphs forward |
{ |
paragraphs backward |
Ctrl-f |
Smart page forward (Ctrl-f / Ctrl-d) |
Ctrl-b |
Smart page backward (C-b / C-u) |
Ctrl-e |
Smart scroll down (3 Ctrl-e/j) |
Ctrl-y |
Smart scroll up (3Ctrl-y/k) |
Native functions
When vimcompatible is not enabled, some native key bindings of vim has been overrided. To use these key bindings, SpaceVim provides alternate key bindings:
| Key bindings | Mode | Action |
|---|---|---|
<Leader> q r |
Normal | Same as native q |
<Leader> q r / |
Normal | Same as native q /, open cmdwin |
<Leader> q r ? |
Normal | Same as native q ?, open cmdwin |
<Leader> q r : |
Normal | Same as native q :, open cmdwin |
Command line mode key bindings
After pressing :, you can switch to command line mode, here is a list of key bindings
can be used in command line mode:
| Key bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
Ctrl-a |
move cursor to beginning |
Ctrl-b |
Move cursor backward in command line |
Ctrl-f |
Move cursor forward in command line |
Ctrl-w |
delete a whole word |
Ctrl-u |
remove all text before cursor |
Ctrl-k |
remove all text after cursor |
Ctrl-c/Esc |
cancel command line mode |
Tab |
next item in popup menu |
Shift-Tab |
previous item in popup menu |
Mappings guide
A guide buffer is displayed each time the prefix key is pressed in normal mode. It lists the available key bindings and their short descriptions.
The prefix can be [SPC], [WIN] and <Leader>.
The default keys of these prefixs are:
| Prefix name | Custom options and default values | Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
[SPC] |
NONE / <Space> |
default mapping prefix of SpaceVim |
[WIN] |
windows_leader / s |
window mapping prefix of SpaceVim |
<Leader> |
default vim leader | default leader prefix of vim/Neovim |
The default value of <Leader> is \, if you want to change this key,
you need to use bootstrap function. For example, use , as the <Leader> key:
function! myspacevim#before() abort
let g:mapleader = ','
endfunction
NOTE: When changing valuable g:mapleader in a function.
you can not omit the valuable scope. Because the default scope
of a valuable in function is l:. It seems different from what you
seee in vim help :h mapleader.
By default the guide buffer will be displayed 1000ms after the keys being pressed.
You can change the delay by adding vim option 'timeoutlen' to your bootstrap function.
For example, after pressing <Space> in normal mode, you will see:
This guide shows you all the available key bindings begin with [SPC], you can type b for all the buffer mappings, p for project mappings, etc.
After pressing Ctrl-h in guide buffer, you will get paging and help info in the statusline.
| Keys | Descriptions |
|---|---|
u |
undo pressing |
n |
next page of guide buffer |
p |
previous page of guide buffer |
Use SpaceVim#custom#SPC() to define custom SPC mappings. For instance:
call SpaceVim#custom#SPC('nnoremap', ['f', 't'], 'echom "hello world"', 'test custom SPC', 1)
Fuzzy find key bidnings
It is possible to search for specific key bindings by pressing ? in the root of guide buffer.
To narrow the list, just insert the mapping keys or descriptions of what mappings you want, Unite/Denite will fuzzy find the mappings, to find buffer related mappings:
Then use <Tab> or <Up> and <Down> to select the mapping, press <Enter> to execute that command.
Editing
Moving text
| Key | Action |
|---|---|
> / Tab |
Indent to right and re-select |
< / Shift-Tab |
Indent to left and re-select |
Ctrl-Shift-Up |
move lines up |
Ctrl-Shift-Down |
move lines down |
Code indentation
The default indentation of code is 2, which is controlled by option default_indent.
If you prefer to use 4 as code indentation. Just add following snippet into SpaceVim
configuration file:
[options]
default_indent = 4
The default_indent option will be applied to vim's &tabstop, &softtabstop and
&shiftwidth options. By default, when user insert a <Tab>, it will be expanded
to spaces. This feature can be disabled by expand_tab option.
[options]
default_indent = 4
expand_tab = true
Text manipulation commands
Text related commands (start with x):
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC x a # |
align region at # |
SPC x a % |
align region at % |
SPC x a & |
align region at & |
SPC x a ( |
align region at ( |
SPC x a ) |
align region at ) |
SPC x a [ |
align region at [ |
SPC x a ] |
align region at ] |
SPC x a { |
align region at { |
SPC x a } |
align region at } |
SPC x a , |
align region at , |
SPC x a . |
align region at . (for numeric tables) |
SPC x a : |
align region at : |
SPC x a ; |
align region at ; |
SPC x a = |
align region at = |
SPC x a ¦ |
align region at ¦ |
| `SPC x a | ` |
SPC x a SPC |
align region at [SPC] |
SPC x a a |
align region (or guessed section) using default rules (TODO) |
SPC x a c |
align current indentation region using default rules (TODO) |
SPC x a l |
left-align with evil-lion (TODO) |
SPC x a L |
right-align with evil-lion (TODO) |
SPC x a r |
align region at user-specified regexp |
SPC x a o |
align region at operators +-*/ etc |
SPC x c |
count the number of chars/words/lines in the selection region |
SPC x d w |
delete trailing whitespaces |
SPC x d SPC |
Delete all spaces and tabs around point, leaving one space |
SPC x g l |
set languages used by translate commands (TODO) |
SPC x g t |
translate current word using Google Translate |
SPC x g T |
reverse source and target languages (TODO) |
SPC x i c |
change symbol style to lowerCamelCase |
SPC x i C |
change symbol style to UpperCamelCase |
SPC x i i |
cycle symbol naming styles (i to keep cycling) |
SPC x i - |
change symbol style to kebab-case |
SPC x i k |
change symbol style to kebab-case |
SPC x i _ |
change symbol style to under_score |
SPC x i u |
change symbol style to under_score |
SPC x i U |
change symbol style to UP_CASE |
SPC x j c |
set the justification to center |
SPC x j f |
set the justification to full (TODO) |
SPC x j l |
set the justification to left |
SPC x j n |
set the justification to none (TODO) |
SPC x j r |
set the justification to right |
SPC x J |
move down a line of text (enter transient state) |
SPC x K |
move up a line of text (enter transient state) |
SPC x l d |
duplicate line or region (TODO) |
SPC x l s |
sort lines (TODO) |
SPC x l u |
uniquify lines (TODO) |
SPC x o |
use avy to select a link in the frame and open it (TODO) |
SPC x O |
use avy to select multiple links in the frame and open them (TODO) |
SPC x t c |
swap (transpose) the current character with the previous one |
SPC x t C |
swap (transpose) the current character with the next one |
SPC x t w |
swap (transpose) the current word with the previous one |
SPC x t W |
swap (transpose) the current word with the next one |
SPC x t l |
swap (transpose) the current line with the previous one |
SPC x t L |
swap (transpose) the current line with the next one |
SPC x u |
set the selected text to lower case |
SPC x U |
set the selected text to upper case |
SPC x w c |
count the words in the select region |
SPC x w d |
show dictionary entry of word from wordnik.com (TODO) |
SPC x <Tab> |
indent or dedent a region rigidly (TODO) |
Text insertion commands
Text insertion commands (start with i):
| Key bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC i l l |
insert lorem-ipsum list |
SPC i l p |
insert lorem-ipsum paragraph |
SPC i l s |
insert lorem-ipsum sentence |
SPC i p 1 |
insert simple password |
SPC i p 2 |
insert stronger password |
SPC i p 3 |
insert password for paranoids |
SPC i p p |
insert a phonetically easy password |
SPC i p n |
insert a numerical password |
SPC i u |
Search for Unicode characters and insert them into the active buffer. |
SPC i U 1 |
insert UUIDv1 (use universal argument to insert with CID format) |
SPC i U 4 |
insert UUIDv4 (use universal argument to insert with CID format) |
SPC i U U |
insert UUIDv4 (use universal argument to insert with CID format) |
Tips: You can specify number of password characters using prefix argument, (i.e. 10 SPC i p 1 will generate 10 characters of simple password)
Expand regions of text
Key bindings available in visual mode:
| Key bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
v |
expand visual selection of text to larger region |
V |
shrink visual selection of text to smaller region |
Increase/Decrease numbers
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC n + |
increase the number under point by one and initiate transient state |
SPC n - |
decrease the number under point by one and initiate transient state |
In transient state:
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
+ |
increase the number under point by one |
- |
decrease the number under point by one |
| Any other key | leave the transient state |
Tips: You can increase or decrease a number by more than once by using a prefix argument (i.e. 10 SPC n + will add 10 to the number under cursor).
Copy and paste
If has('unnamedplus'), the register used by <Leader> y is +, otherwise it is *.
Read :h registers for more info about other registers.
| Key | Descriptions |
|---|---|
<Leader> y |
Copy text to system clipboard |
<Leader> p |
Paste text from system clipboard after here |
<Leader> P |
Paste text from system clipboard before here |
<Leader> Y |
Copy text to pastebin |
The <Leader> Y key binding will copy selected text to a pastebin server. It requires curl in your $PATH.
And the default command is:
curl -s -F "content=<-" http://dpaste.com/api/v2/
This command will read stdin and copy the stdin to dpaste server. It is same as:
echo "selected text" | curl -s -F "content=<-" http://dpaste.com/api/v2/
Commenting
Comments are handled by nerdcommenter, it’s bound to the following keys.
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC ; |
comment operator |
SPC c a |
switch to the alternative set of delimiters |
SPC c h |
hide/show comments |
SPC c l |
toggle comment lines |
SPC c L |
comment lines |
SPC c u |
uncomment lines |
SPC c p |
toggle comment paragraphs |
SPC c P |
comment paragraphs |
SPC c s |
comment with pretty layout |
SPC c t |
toggle comment to line |
SPC c T |
comment to line |
SPC c y |
toggle comment and yank(TODO) |
SPC c Y |
yank and comment |
SPC c $ |
comment current line from cursor to the end of the line |
Tips: SPC ; will start operator mode, in this mode, you can use motion command to comment lines.
For example, SPC ; 4 j will comment current line and the following 4 lines.
Undo tree
Undo tree visualizes undo history and makes it easier to browse and switch between different undo branches.
The default key binding is F7. If +python or +python3 is enabled, mundo will be loaded,
otherwise undotree will be loaded.
Key bindings within undo tree windows:
| key bindings | description |
|---|---|
G |
move_bottom |
J |
move_older_write |
K |
move_newer_write |
N |
previous_match |
P |
play_to |
<2-LeftMouse> |
mouse_click |
/ |
search |
<CR> |
preview |
d |
diff |
<down> |
move_older |
<up> |
move_newer |
i |
toggle_inline |
j |
move_older |
k |
move_newer |
n |
next_match |
o |
preview |
p |
diff_current_buffer |
q |
quit |
r |
diff |
gg |
move_top |
? |
toggle_help |
Multi-Encodings
SpaceVim uses utf-8 as default encoding. There are four options for these case:
- fileencodings (fencs): ucs-bom,utf-8,default,latin1
- fileencoding (fenc): utf-8
- encoding (enc): utf-8
- termencoding (tenc): utf-8 (only supported in Vim)
To fix messy display: SPC e a is the mapping for auto detect the file encoding. After detecting file encoding, you can run the command below to fix the encoding:
set enc=utf-8
write
Window manager
Window manager key bindings can only be used in normal mode. The default leader [WIN] is s, you
can change it via windows_leader option:
[options]
windows_leader = "s"
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
q |
Smart buffer close |
WIN v |
:split |
WIN V |
Split with previous buffer |
WIN g |
:vsplit |
WIN G |
Vertically split with previous buffer |
WIN t |
Open new tab (:tabnew) |
WIN o |
Close other windows (:only) |
WIN x |
Remove buffer, leave blank window |
WIN q |
Remove current buffer |
WIN Q |
Close current buffer (:close) |
Shift-Tab |
Switch to alternate window (switch back and forth) |
SpaceVim has mapped normal q as smart buffer close, the normal func of q
can be get by <Leader> q r, if you want to disable this feature, you can use vimcompatible mode.
General Editor windows
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
<F2> |
Toggle tagbar |
<F3> |
Toggle Vimfiler |
Ctrl-Down |
Move to split below (Ctrl-w j) |
Ctrl-Up |
Move to upper split (Ctrl-w k) |
Ctrl-Left |
Move to left split (Ctrl-w h) |
Ctrl-Right |
Move to right split (Ctrl-w l) |
Window manipulation key bindings
Every window has a number displayed at the start of the statusline and can be quickly accessed using SPC number.
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC 1 |
go to window number 1 |
SPC 2 |
go to window number 2 |
SPC 3 |
go to window number 3 |
SPC 4 |
go to window number 4 |
SPC 5 |
go to window number 5 |
SPC 6 |
go to window number 6 |
SPC 7 |
go to window number 7 |
SPC 8 |
go to window number 8 |
SPC 9 |
go to window number 9 |
Windows manipulation commands (start with w):
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC w . |
windows transient state |
SPC w <Tab> |
switch to alternate window in the current frame (switch back and forth) |
SPC w = |
balance split windows |
SPC w b |
force the focus back to the minibuffer (TODO) |
SPC w c |
Distraction-free reading current window (tools layer) |
SPC w C |
Distraction-free reading other windows via vim-choosewin (tools layer) |
SPC w d |
delete a window |
SPC u SPC w d |
delete a window and its current buffer (does not delete the file) (TODO) |
SPC w D |
delete another window using vim-choosewin |
SPC u SPC w D |
delete another window and its current buffer using vim-choosewin (TODO) |
SPC w t |
toggle window dedication (dedicated window cannot be reused by a mode) (TODO) |
SPC w f |
toggle follow mode (TODO) |
SPC w F |
create new tab(frame) |
SPC w h |
move to window on the left |
SPC w H |
move window to the left |
SPC w j |
move to window below |
SPC w J |
move window to the bottom |
SPC w k |
move to window above |
SPC w K |
move window to the top |
SPC w l |
move to window on the right |
SPC w L |
move window to the right |
SPC w m |
maximize/minimize a window (maximize is equivalent to delete other windows) (TODO, now only support maximize) |
SPC w M |
swap windows using vim-choosewin |
SPC w o |
cycle and focus between tabs |
SPC w p m |
open messages buffer in a popup window (TODO) |
SPC w p p |
close the current sticky popup window (TODO) |
SPC w r |
rotate windows forward |
SPC w R |
rotate windows backward |
SPC w s / SPC w - |
horizontal split |
SPC w S |
horizontal split and focus new window |
SPC w u |
undo window layout (used to effectively undo a closed window) (TODO) |
SPC w U |
redo window layout (TODO) |
SPC w v / SPC w / |
vertical split |
SPC w V |
vertical split and focus new window |
SPC w w |
cycle and focus between windows |
SPC w W |
select window using vim-choosewin |
SPC w x |
exchange current window with next one |
Buffers and Files
Buffers manipulation key bindings
Buffer manipulation commands (start with b):
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC <Tab> |
switch to alternate buffer in the current window (switch back and forth) |
SPC b . |
buffer transient state |
SPC b b |
switch to a buffer (via denite/unite) |
SPC b d |
kill the current buffer (does not delete the visited file) |
SPC u SPC b d |
kill the current buffer and window (does not delete the visited file) (TODO) |
SPC b D |
kill a visible buffer using vim-choosewin |
SPC u SPC b D |
kill a visible buffer and its window using ace-window(TODO) |
SPC b Ctrl-d |
kill other buffers |
SPC b Ctrl-D |
kill buffers using a regular expression(TODO) |
SPC b e |
erase the content of the buffer (ask for confirmation) |
SPC b h |
open SpaceVim home buffer |
SPC b n |
switch to next buffer avoiding special buffers |
SPC b m |
open Messages buffer |
SPC u SPC b m |
kill all buffers and windows except the current one(TODO) |
SPC b p |
switch to previous buffer avoiding special buffers |
SPC b P |
copy clipboard and replace buffer (useful when pasting from a browser) |
SPC b R |
revert the current buffer (reload from disk) |
SPC b s |
switch to the scratch buffer (create it if needed) |
SPC b w |
toggle read-only (writable state) |
SPC b Y |
copy whole buffer to clipboard (useful when copying to a browser) |
z f |
Make current function or comments visible in buffer as much as possible (TODO) |
Create a new empty buffer
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC b N h |
create new empty buffer in a new window on the left |
SPC b N j |
create new empty buffer in a new window at the bottom |
SPC b N k |
create new empty buffer in a new window above |
SPC b N l |
create new empty buffer in a new window below |
SPC b N n |
create new empty buffer in current window |
Special Buffers
In SpaceVim, there are many special buffers, these buffers are created by plugins or SpaceVim itself. And these buffers are not listed.
Files manipulations key bindings
Files manipulation commands (start with f):
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC f / |
Find files with find or fd command |
SPC f b |
go to file bookmarks |
SPC f c |
copy current file to a different location(TODO) |
SPC f C d |
convert file from unix to dos encoding |
SPC f C u |
convert file from dos to unix encoding |
SPC f D |
delete a file and the associated buffer with confirmation |
SPC f E |
open a file with elevated privileges (sudo layer) (TODO) |
SPC f W |
save a file with elevated privileges (sudo layer) |
SPC f f |
open file |
SPC f F |
try to open the file under point |
SPC f o |
Find current file in file tree |
SPC f R |
rename the current file(TODO) |
SPC f s |
save a file |
SPC f S |
save all files |
SPC f r |
open a recent file |
SPC f t |
toggle file tree side bar |
SPC f T |
show file tree side bar |
SPC f d |
toggle disk manager in Windows OS |
SPC f y |
show and copy current file absolute path in the cmdline |
SPC f Y |
show and copy remote url of current file |
NOTE: If you are using window, you need to install findutils or fd.
If you are using scoop to install packages, the commands in C:\WINDOWS\system32 will override User path.
so you need to put the scoop binary PATH before all the windows C:\WINDOWS\system32 PATH.
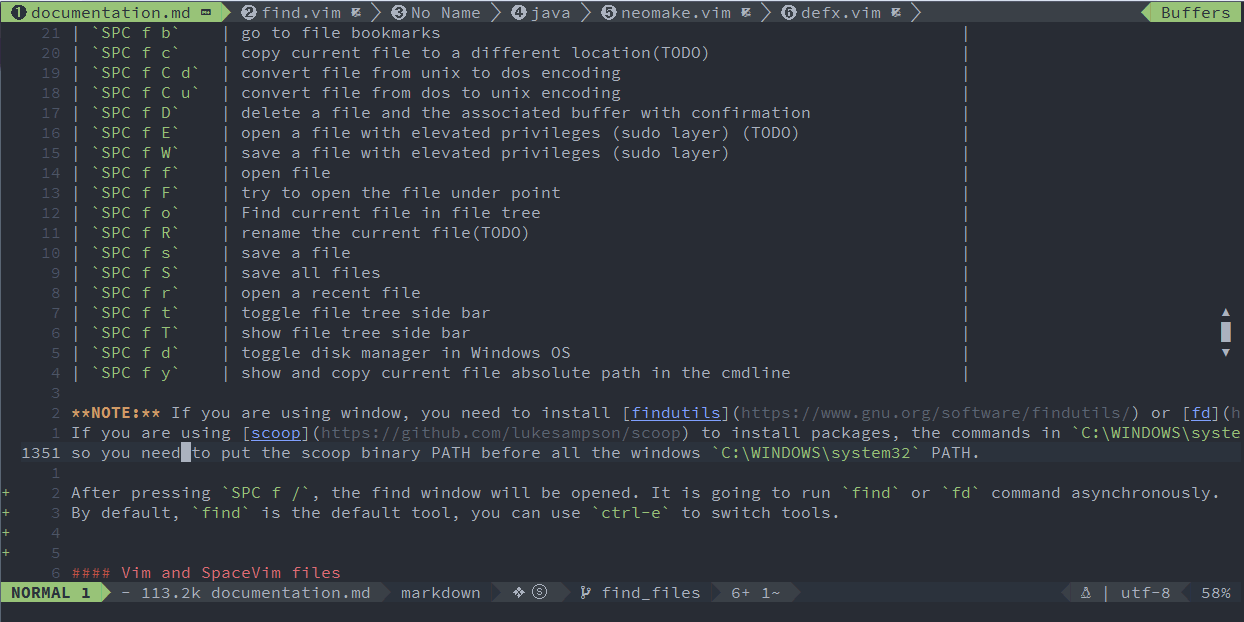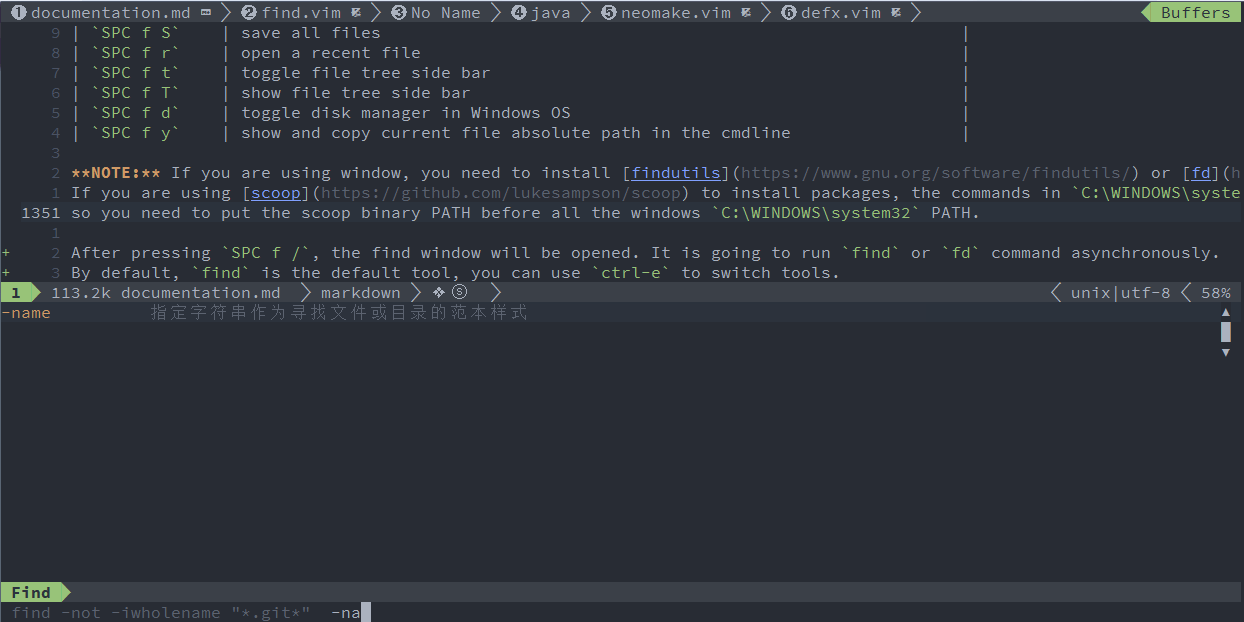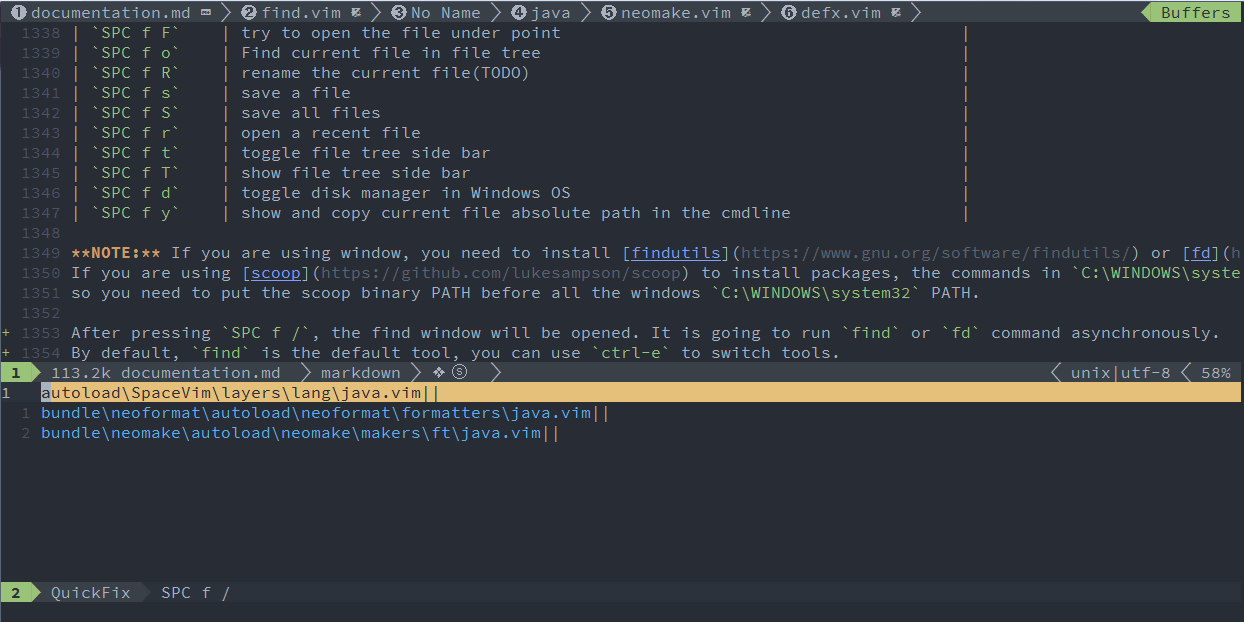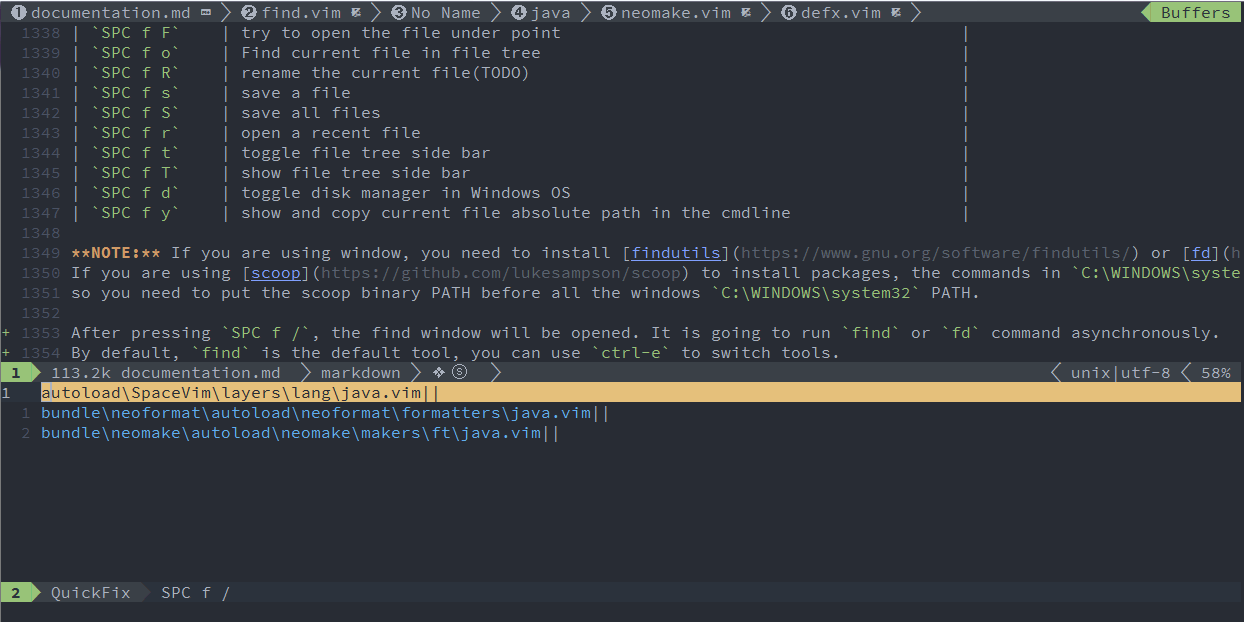
After pressing SPC f /, the find window will be opened. It is going to run find or fd command asynchronously.
By default, find is the default tool, you can use ctrl-e to switch tools.
Vim and SpaceVim files
Convenient key bindings are located under the prefix SPC f v to quickly navigate between Vim and SpaceVim specific files.
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC f v v |
display and copy SpaceVim version |
SPC f v d |
open SpaceVim custom configuration file |
Available layers
All layers can be easily discovered via :SPLayer -l accessible with SPC h l.
Available plugins in SpaceVim
All plugins can be easily discovered via <Leader> f p.
Fuzzy finder
SpaceVim provides five fuzzy find tools, each of them is configured in a layer
(unite, denite, leaderf, ctrlp and fzf layer).
These layers have the same key bindings and features. But they need different dependencies.
Users only need to load one of these layers, they will be able to get these features.
for example, load the denite layer:
[[layers]]
name = "denite"
Key bindings
| Key bindings | Discription |
|---|---|
<Leader> f <Space> |
Fuzzy find menu:CustomKeyMaps |
<Leader> f p |
Fuzzy find menu:AddedPlugins |
<Leader> f e |
Fuzzy find register |
<Leader> f h |
Fuzzy find history/yank |
<Leader> f j |
Fuzzy find jump, change |
<Leader> f l |
Fuzzy find location list |
<Leader> f m |
Fuzzy find output messages |
<Leader> f o |
Fuzzy find outline |
<Leader> f q |
Fuzzy find quick fix |
<Leader> f r |
Resumes Unite window |
Differences between these layers
The above key bindings are only part of fuzzy finder layers, please read the layers's documentations.
| Feature | denite | unite | leaderf | ctrlp | fzf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CustomKeyMaps menu | yes | yes | yes | no | no |
| AddedPlugins menu | yes | yes | yes | no | no |
| register | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| file | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| yank history | yes | yes | yes | no | yes |
| jump | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| location list | yes | yes | yes | no | yes |
| outline | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| message | yes | yes | yes | no | yes |
| quickfix list | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| resume windows | yes | yes | yes | no | no |
Key bindings within fuzzy finder buffer
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
<Tab> / Ctrl-j |
Select next line |
Shift-Tab / Ctrl-k |
Select previous line |
<Esc> |
Leave Insert mode |
Ctrl-w |
Delete backward path |
Ctrl-u |
Delete whole line before cursor |
<Enter> |
Run default action |
Ctrl-s |
Open in a split |
Ctrl-v |
Open in a vertical split |
Ctrl-t |
Open in a new tab |
Ctrl-g |
Close fuzzy finder |
With an external tool
SpaceVim can be interfaced with different searching tools like:
The search commands in SpaceVim are organized under the SPC s
prefix with the next key is the tool to use and the last key is the scope.
For instance, SPC s a b will search in all opened buffers using ag.
If the last key (determining the scope) is uppercase then the
current word under the cursor is used as default input for the search.
For instance, SPC s a B will search the word under cursor.
If the tool key is omitted then a default tool will be automatically selected for the search.
This tool corresponds to the first tool found on the system of the list search_tools,
the default order is ['rg', 'ag', 'pt', 'ack', 'grep', 'findstr', 'git'].
For instance SPC s b will search in the opened buffers using pt if rg and ag have not been found on the system.
The tool keys are:
| Tool | Key |
|---|---|
| ag | a |
| grep | g |
| git grep | G |
| ack | k |
| rg | r |
| pt | t |
The available scopes and corresponding keys are:
| Scope | Key |
|---|---|
| opened buffers | b |
| buffer directory | d |
| files in a given directory | f |
| current project | p |
It is possible to search in the current file by double pressing the second key of the sequence, for instance SPC s a a will search in the current file with ag.
Notes:
rg,agandptare optimized to be used in a source control repository but they can be used in an arbitrary directory as well.- It is also possible to search in several directories at once by marking them in the unite buffer.
Beware if you use pt, TCL parser tools also install a command line tool called pt.
Custom searching tool
To change the options of a search tool, you need to use the bootstrap function.
The following example shows how to change the default option of searching tool rg.
function! myspacevim#before() abort
let profile = SpaceVim#mapping#search#getprofile('rg')
let default_opt = profile.default_opts + ['--no-ignore-vcs']
call SpaceVim#mapping#search#profile({'rg' : {'default_opts' : default_opt}})
endfunction
The structure of searching tool profile is:
" { 'ag' : {
" 'namespace' : '', " a single char a-z
" 'command' : '', " executable
" 'default_opts' : [], " default options
" 'recursive_opt' : [], " default recursive options
" 'expr_opt' : '', " option for enable expr mode
" 'fixed_string_opt' : '', " option for enable fixed string mode
" 'ignore_case' : '', " option for enable ignore case mode
" 'smart_case' : '', " option for enable smart case mode
" }
" }
Useful key bindings
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC r l |
resume the last completion buffer |
SPC s ` |
go back to the previous place before jump |
| Prefix argument | will ask for file extensions |
Searching in current file
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC s s |
search with the first found tool |
SPC s S |
search with the first found tool with default input |
SPC s a a |
ag |
SPC s a A |
ag with default input |
SPC s g g |
grep |
SPC s g G |
grep with default input |
SPC s r r |
rg |
SPC s r R |
rg with default input |
Searching in buffer directory
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC s d |
searching in buffer directory with default tool |
SPC s D |
searching in buffer directory cursor word with default tool |
SPC s a d |
searching in buffer directory with ag |
SPC s a D |
searching in buffer directory cursor word with ag |
SPC s g d |
searching in buffer directory with grep |
SPC s g D |
searching in buffer directory cursor word with grep |
SPC s G d |
searching in buffer directory with git-grep |
SPC s G D |
searching in buffer directory cursor word with git-grep |
SPC s k d |
searching in buffer directory with ack |
SPC s k D |
searching in buffer directory cursor word with ack |
SPC s r d |
searching in buffer directory with rg |
SPC s r D |
searching in buffer directory cursor word with rg |
SPC s t d |
searching in buffer directory with pt |
SPC s t D |
searching in buffer directory cursor word with pt |
Searching in all loaded buffers
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC s b |
search with the first found tool |
SPC s B |
search with the first found tool with default input |
SPC s a b |
ag |
SPC s a B |
ag with default input |
SPC s g b |
grep |
SPC s g B |
grep with default input |
SPC s G b |
git-grep |
SPC s G B |
git-grep with default input |
SPC s k b |
ack |
SPC s k B |
ack with default input |
SPC s r b |
rg |
SPC s r B |
rg with default input |
SPC s t b |
pt |
SPC s t B |
pt with default input |
Searching in an arbitrary directory
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC s f |
search with the first found tool |
SPC s F |
search with the first found tool with default input |
SPC s a f |
ag |
SPC s a F |
ag with default text |
SPC s g f |
grep |
SPC s g F |
grep with default text |
SPC s G f |
git-grep |
SPC s G F |
git-grep with default text |
SPC s k f |
ack |
SPC s k F |
ack with default text |
SPC s r f |
rg |
SPC s r F |
rg with default text |
SPC s t f |
pt |
SPC s t F |
pt with default text |
Searching in a project
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC s p |
search with the first found tool |
SPC s P |
search with the first found tool with default input |
SPC s a p |
ag |
SPC s a P |
ag with default text |
SPC s g p |
grep |
SPC s g p |
grep with default text |
SPC s k p |
ack |
SPC s k P |
ack with default text |
SPC s t p |
pt |
SPC s t P |
pt with default text |
SPC s r p |
rg |
SPC s r P |
rg with default text |
Hint: It is also possible to search in a project without needing to open a file beforehand.
To do so use SPC p p and then C-s on a given project to directly search into it like with SPC s p. (TODO)
Background searching in a project
Background search keyword in a project, when searching done, the count will be shown on the statusline.
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC s j |
searching input expr background with the first found tool |
SPC s J |
searching cursor word background with the first found tool |
SPC s l |
List all searching result in quickfix buffer |
SPC s a j |
ag |
SPC s a J |
ag with default text |
SPC s g j |
grep |
SPC s g J |
grep with default text |
SPC s k j |
ack |
SPC s k J |
ack with default text |
SPC s t j |
pt |
SPC s t J |
pt with default text |
SPC s r j |
rg |
SPC s r J |
rg with default text |
Searching the web
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC s w g |
Get Google suggestions in Vim. Opens Google results in Browser. |
SPC s w w |
Get Wikipedia suggestions in Vim. Opens Wikipedia page in Browser.(TODO) |
Note: to enable google suggestions in Vim, you need to add enable_googlesuggest = 1 to your custom Configuration file.
Searching on the fly
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC s / |
Searching in project on the fly with default tools |
Key bindings in FlyGrep buffer:
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
<Esc> |
close FlyGrep buffer |
<Enter> |
open file at the cursor line |
Ctrl-t |
open item in new tab |
Ctrl-s |
open item in split window |
Ctrl-v |
open item in vertical split window |
Ctrl-q |
apply all items into quickfix |
<Tab> |
move cursor line down |
Shift-<Tab> |
move cursor line up |
<BackSpace> |
remove last character |
Ctrl-w |
remove the Word before the cursor |
Ctrl-u |
remove the Line before the cursor |
Ctrl-k |
remove the Line after the cursor |
Ctrl-a / <Home> |
Go to the beginning of the line |
Ctrl-e / <End> |
Go to the end of the line |
Persistent highlighting
SpaceVim uses search_highlight_persist to keep the searched expression highlighted until the next search. It is also possible to clear the highlighting by pressing SPC s c or executing the ex command :noh.
Getting help
Fuzzy finder layer is powerful tool to unite all interfaces. It is meant to be like Helm for Vim. These mappings are for getting help info about functions, variables etc:
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC h SPC |
discover SpaceVim documentation, layers and packages using fuzzy finder layer |
SPC h i |
get help with the symbol at point |
SPC h k |
show top-level bindings with which-key |
SPC h m |
search available man pages |
Reporting an issue:
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC h I |
Open SpaceVim GitHub issue page with pre-filled information |
Unimpaired bindings
| Mappings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
[ SPC |
Insert space above |
] SPC |
Insert space below |
[ b |
Go to previous buffer |
] b |
Go to next buffer |
[ n |
Go to previous conflict marker |
] n |
Go to next conflict marker |
[ f |
Go to previous file in directory |
] f |
Go to next file in directory |
[ l |
Go to the previous error |
] l |
Go to the next error |
[ c |
Go to the previous vcs hunk (need VersionControl layer) |
] c |
Go to the next vcs hunk (need VersionControl layer) |
[ q |
Go to the previous error |
] q |
Go to the next error |
[ t |
Go to the previous frame |
] t |
Go to the next frame |
[ w |
Go to the previous window |
] w |
Go to the next window |
[ e |
Move line up |
] e |
Move line down |
[ p |
Paste above current line |
] p |
Paste below current line |
g p |
Select pasted text |
Jumping, Joining and Splitting
The SPC j prefix is for jumping, joining and splitting.
Jumping
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC j 0 |
go to the beginning of line (and set a mark at the previous location in the line) |
SPC j $ |
go to the end of line (and set a mark at the previous location in the line) |
SPC j b |
jump backward |
SPC j f |
jump forward |
SPC j d |
jump to a listing of the current directory |
SPC j D |
jump to a listing of the current directory (other window) |
SPC j i |
jump to a definition in buffer (denite outline) |
SPC j I |
jump to a definition in any buffer (denite outline) |
SPC j j |
jump to a character in the buffer (easymotion) |
SPC j J |
jump to a suite of two characters in the buffer (easymotion) |
SPC j k |
jump to next line and indent it using auto-indent rules |
SPC j l |
jump to a line with avy (easymotion) |
SPC j q |
show the dumb-jump quick look tooltip (TODO) |
SPC j u |
jump to a URL in the current window |
SPC j v |
jump to the definition/declaration of an Emacs Lisp variable (TODO) |
SPC j w |
jump to a word in the current buffer (easymotion) |
Joining and splitting
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
J |
join the current line with the next line |
SPC j o |
join a code block into a single-line statement |
SPC j m |
split a one-liner into multiple lines |
SPC j k |
go to next line and indent it using auto-indent rules |
SPC j n |
split the current line at point, insert a new line and auto-indent |
SPC j o |
split the current line at point but let point on current line |
SPC j s |
split a quoted string or s-expression in place |
SPC j S |
split a quoted string or s-expression with \n, and auto-indent the new line |
Other key bindings
Commands starting with g
After pressing prefix g in normal mode, if you do not remember the mappings, you will see the guide
which will tell you the functional of all mappings starting with g.
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
g # |
search under cursor backward |
g $ |
go to rightmost character |
g & |
repeat last ":s" on all lines |
g ' |
jump to mark |
g * |
search under cursor forward |
g + |
newer text state |
g , |
newer position in change list |
g - |
older text state |
g / |
stay incsearch |
g 0 |
go to leftmost character |
g ; |
older position in change list |
g < |
last page of previous command output |
g <Home> |
go to leftmost character |
g E |
end of previous word |
g F |
edit file under cursor(jump to line after name) |
g H |
select line mode |
g I |
insert text in column 1 |
g J |
join lines without space |
g N |
visually select previous match |
g Q |
switch to Ex mode |
g R |
enter VREPLACE mode |
g T |
previous tag page |
g U |
make motion text uppercase |
g ] |
tselect cursor tag |
g ^ |
go to leftmost no-white character |
g _ |
go to last char |
g ` |
jump to mark |
g a |
print ascii value of cursor character |
g d |
goto definition |
g e |
go to end of previous word |
g f |
edit file under cursor |
g g |
go to line N |
g h |
select mode |
g i |
insert text after '^ mark |
g j |
move cursor down screen line |
g k |
move cursor up screen line |
g m |
go to middle of screenline |
g n |
visually select next match |
g o |
goto byte N in the buffer |
g p |
Select last paste |
g s |
sleep N seconds |
g t |
next tag page |
g u |
make motion text lowercase |
g ~ |
swap case for Nmove text |
g <End> |
go to rightmost character |
g Ctrl-g |
show cursor info |
Commands starting with z
After pressing prefix z in normal mode, if you do not remember the mappings, you will see the guide
which will tell you the functional of all mappings starting with z.
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
z <Right> |
scroll screen N characters to left |
z + |
cursor to screen top line N |
z - |
cursor to screen bottom line N |
z . |
cursor line to center |
z <Enter> |
cursor line to top |
z = |
spelling suggestions |
z A |
toggle folds recursively |
z C |
close folds recursively |
z D |
delete folds recursively |
z E |
eliminate all folds |
z F |
create a fold for N lines |
z G |
mark good spelled (update internal wordlist) |
z H |
scroll half a screenwidth to the right |
z L |
scroll half a screenwidth to the left |
z M |
set foldlevel to zero |
z N |
set foldenable |
z O |
open folds recursively |
z R |
set foldlevel to deepest fold |
z W |
mark wrong spelled (update internal wordlist) |
z X |
re-apply foldlevel |
z ^ |
cursor to screen bottom line N |
z a |
toggle a fold |
z b |
redraw, cursor line at bottom |
z c |
close a fold |
z d |
delete a fold |
z e |
right scroll horizontally to cursor position |
z f |
create a fold for motion |
z g |
mark good spelled |
z h |
scroll screen N characters to right |
z i |
toggle foldenable |
z j |
mode to start of next fold |
z k |
mode to end of previous fold |
z l |
scroll screen N characters to left |
z m |
subtract one from foldlevel |
z n |
reset foldenable |
z o |
open fold |
z r |
add one to foldlevel |
z s |
left scroll horizontally to cursor position |
z t |
cursor line at top of window |
z v |
open enough folds to view cursor line |
z w |
mark wrong spelled |
z x |
re-apply foldlevel and do "zV" |
z z |
smart scroll |
z <Left> |
scroll screen N characters to right |
Advanced usage
Managing projects
When open a file, SpaceVim will change current directory to the project
root directory which contains this file. The project root directory detection
is based on on project_rooter_patterns option, and the default value is:
[options]
project_rooter_patterns = ['.git/', '_darcs/', '.hg/', '.bzr/', '.svn/']
The project manager will find the outermost directory by default. To find the nearest directory instead,
you need to change project_rooter_outermost to false:
[options]
project_rooter_patterns = ['.git/', '_darcs/', '.hg/', '.bzr/', '.svn/']
project_rooter_outermost = false
Sometimes we want to ignore some directories when detecting the project root directory.
Add a ! prefix before the pattern.
For example, ignore node_packages/ directory:
[options]
project_rooter_patterns = ['.git/', '_darcs/', '.hg/', '.bzr/', '.svn/', '!node_packages/']
project_rooter_outermost = false
You can also disable project root detection completely (i.e. vim will set the root directory to the present working directory):
[options]
project_rooter_automatically = false
Project manager commands start with p:
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC p ' |
open a shell in project’s root (need the shell layer) |
Searching files in project
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC p f |
find files in current project |
SPC p / |
fuzzy search for text in current project |
SPC p k |
kill all buffers of current project |
SPC p p |
list all projects |
SPC p p will list all the projects history cross vim sessions. By default
only 20 projects will be listed. To increase it, you can change the value
of projects_cache_num.
To disable the cross session cacche, change enable_projects_cache to false.
[options]
enable_projects_cache = true
projects_cache_num = 20
Custom alternate file
To manager the alternate file of the project, you need to create a .project_alt.json file
in the root of your project. Then you can use command :A to jump to the alternate file of
current file. You can also specific the type of alternate file, for example :A doc.
With a bang :A!, SpaceVim will parse the configuration file additionally. If no type specified,
the default type alternate will be used.
here is an example of .project_alt.json:
{
"autoload/SpaceVim/layers/lang/*.vim": {
"doc": "docs/layers/lang/{}.md",
"test": "test/layer/lang/{}.vader"
}
}
Bookmarks management
Bookmarks manager is included in tools layer, to use following key bindings, you need to enable
tools layer:
[[layers]]
name = "tools"
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
m a |
Show list of all bookmarks |
m m |
Toggle bookmark in current line |
m n |
Jump to next bookmark |
m p |
Jump to previous bookmark |
m i |
Annotate bookmark |
As SpaceVim use above bookmarks mappings, so you cannot use a, m, n, p or i registers to mark current position, but other registers should work well.
If you really need to use these registers, you can map <Leader> m to m in your bootstrap function,
then you can use a registers via <Leader> m a.
function! myspacevim#before() abort
nnoremap <silent><Leader>m m
endfunction
Tasks
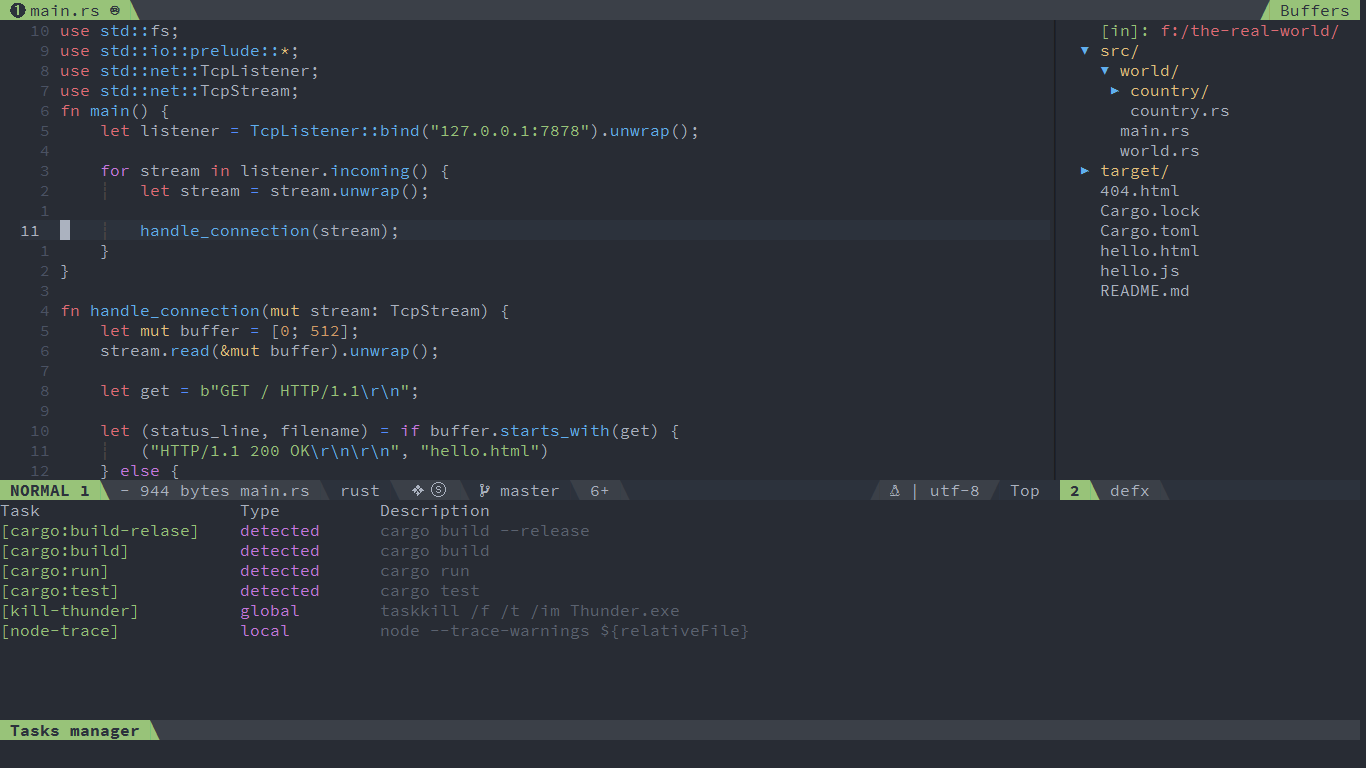
To integrate with external tools, SpaceVim introduce a task manager system, which is similar to vscode tasks-manager. There are two kinds of task configuration file:
~/.SpaceVim.d/tasks.toml: global tasks configuration.SpaceVim.d/tasks.toml: project local tasks configuration
The task defined in global tasks configuration can be overrided by project local tasks configuration.
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC p t e |
edit tasks configuration file |
SPC p t r |
select task to run |
SPC p t l |
list all available tasks |
Custom tasks
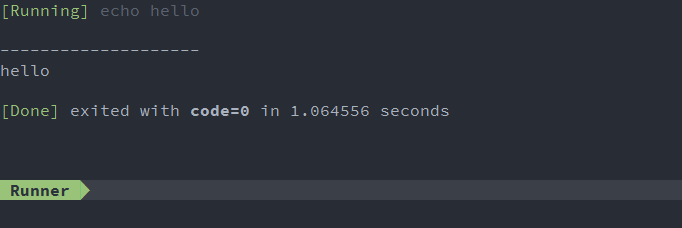
This is basic task configuration for running echo hello world,
and print results to runner windows.
[my-task]
command = 'echo'
args = ['hello world']
To run task in the background, you need to set isBackground to true:
[my-task]
command = 'echo'
args = ['hello world']
isBackground = true
The task's properties have the following semantic:
- command: the actual command to execute.
- args: the arguments passed to the command, it shoud be an array a string list and can be omitted.
- options: override the defaults for
cwd,envorshell. - isBackground:
trueorfalse, specifies whether background running is required, by default, it isfalse. - description: short description of the task
When start a new task, it will kill the previous task. If you want to keep the task
run in background, set isBackground to true.
SpaceVim supports variable substitution in task, The following predefined variables are supported:
- ${workspaceFolder}: - the project root directory
- ${workspaceFolderBasename}: - the parent directory name of current project root
- ${file}: - the path of current file
- ${relativeFile}: - the current file relative to project root
- ${relativeFileDirname}: - the current file's dirname relative to workspaceFolder
- ${fileBasename}: - the current file's basename
- ${fileBasenameNoExtension}: - the current file's basename without file extension
- ${fileDirname}: - the current file's dirname
- ${fileExtname}: - the current file's extension
- ${cwd}: - the task runner's current working directory on startup
- ${lineNumber}: - the current selected line number in the active file
for example: Supposing that you have the following requirements:
A file located at /home/your-username/your-project/folder/file.ext opened in your editor;
The directory /home/your-username/your-project opened as your root workspace.
So you will have the following values for each variable:
- ${workspaceFolder}: -
/home/your-username/your-project/ - ${workspaceFolderBasename}: -
your-project - ${file}: -
/home/your-username/your-project/folder/file.ext - ${relativeFile}: -
folder/file.ext - ${relativeFileDirname}: -
folder/ - ${fileBasename}: -
file.ext - ${fileBasenameNoExtension}: -
file - ${fileDirname}: -
/home/your-username/your-project/folder/ - ${fileExtname}: -
.ext - ${lineNumber}: - line number of the cursor
Task auto-detection
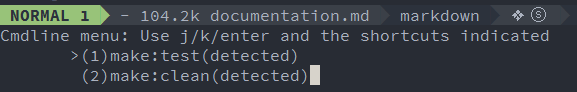
Currently, SpaceVim can auto-detect tasks for npm.
the tasks manager will paser the package.json file for npm systems.
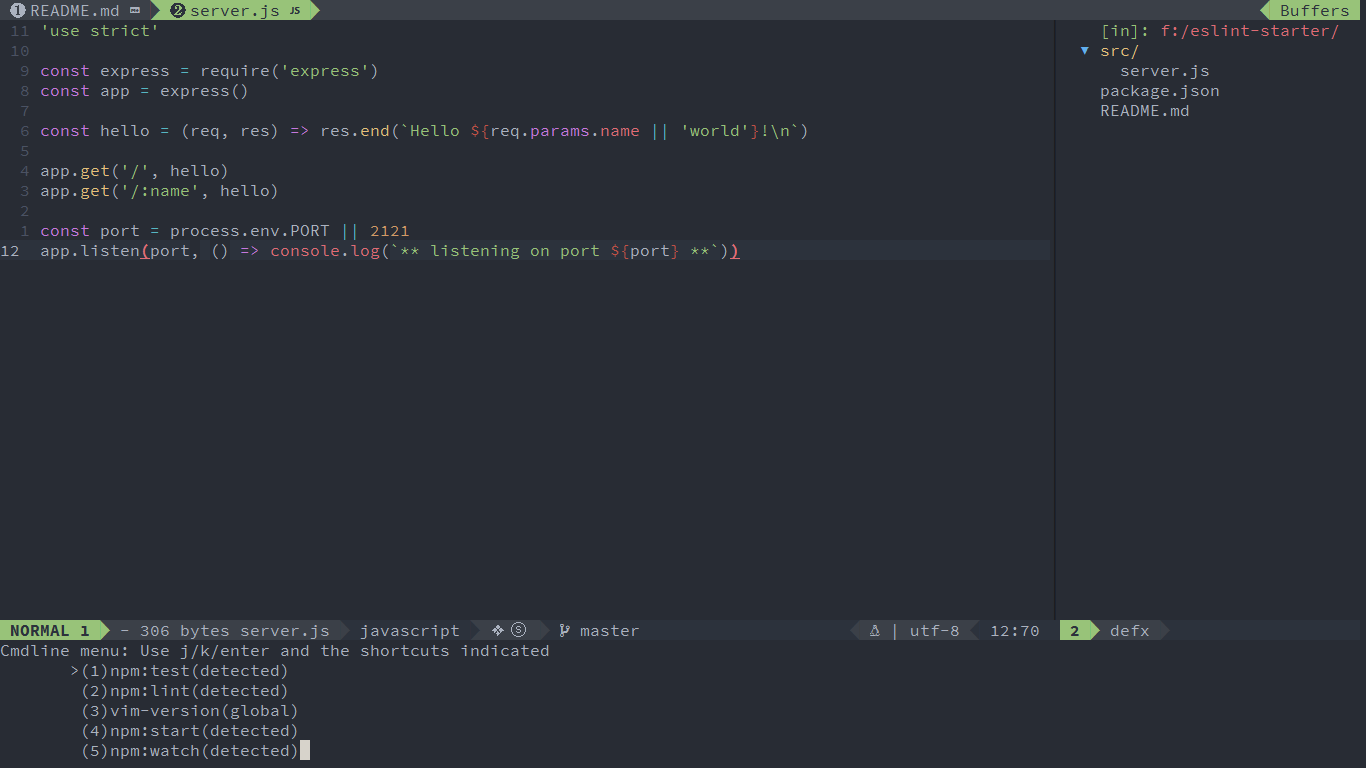
If you have cloned the eslint-starter example,
then pressing SPC p t r shows the following list:
Task provider
Some tasks can be automatically detected by task provider. For example,
a Task Provider could check if there is a specific build file, such as package.json,
and create npm tasks.
To build a task provider, you need to use Bootstrap function. The task provider should be a vim function. and return a task object.
here is an example for building task provider.
function! s:make_tasks() abort
if filereadable('Makefile')
let subcmd = filter(readfile('Makefile', ''), "v:val=~#'^.PHONY'")
if !empty(subcmd)
let commands = split(subcmd[0])[1:]
let conf = {}
for cmd in commands
call extend(conf, {
\ cmd : {
\ 'command': 'make',
\ 'args' : [cmd],
\ 'isDetected' : 1,
\ 'detectedName' : 'make:'
\ }
\ })
endfor
return conf
else
return {}
endif
else
return {}
endif
endfunction
call SpaceVim#plugins#tasks#reg_provider(function('s:make_tasks'))
with above configuration, you will see following tasks in SpaceVim repo:
Replace text with iedit
SpaceVim uses a powerful iedit mode to quick edit multiple occurrences of a symbol or selection.
Two new modes: iedit-Normal/iedit-Insert
The default color for iedit is red/green which is based on the current colorscheme.
iedit states key bindings
State transitions:
| Key Bindings | From | to |
|---|---|---|
SPC s e |
normal or visual | iedit-Normal |
In iedit-Normal mode:
iedit-Normal mode inherits from Normal mode, the following key bindings are specific to iedit-Normal mode.
| Key Binding | Descriptions |
|---|---|
<Esc> |
go back to Normal mode |
i |
switch to iedit-Insert mode, same as i in Normal model |
a |
switch to iedit-Insert mode, same as a in Normal model |
I |
go to the beginning of the current occurrence and switch to iedit-Insert mode, same as I in Normal model |
A |
go to the end of the current occurrence and switch to iedit-Insert mode, same as A in Normal model |
<Left>/h |
Move cursor to left, same as h in Normal model |
<Right>/l |
Move cursor to right, same as l in Normal model |
0/<Home> |
go to the beginning of the current occurrence, same as 0 in Normal model |
$/<End> |
go to the end of the current occurrence, same as $ in Normal model |
C |
delete the characters from the cursor to the end in all occurrences and switch to iedit-Insert mode, same as C in Normal model |
D |
delete the occurrences, same as D in Normal model |
s |
delete the character under cursor and switch to iedit-Insert mode, same as s in Normal model |
S |
delete the occurrences and switch to iedit-Insert mode, same as S in Normal model |
x |
delete the character under cursor in all the occurrences, same as x in Normal model |
X |
delete the character before cursor in all the occurrences, same as X in Normal model |
gg |
go to first occurrence, same as gg in Normal model |
G |
go to last occurrence, same as G in Normal model |
f{char} |
Move the cursor to the right where the {char} first appears in all the occurrences |
n |
go to next occurrence |
N |
go to previous occurrence |
p |
replace occurrences with last yanked (copied) text |
<Tab> |
toggle current occurrence |
In iedit-Insert mode:
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
Ctrl-g / <Esc> |
go back to iedit-Normal mode |
Ctrl-b / <Left> |
move cursor to left |
Ctrl-f / <Right> |
move cursor to right |
Ctrl-a / <Home> |
moves the cursor to the beginning of the current occurrence |
Ctrl-e / <End> |
moves the cursor to the end of the current occurrence |
Ctrl-w |
delete word before cursor |
Ctrl-k |
delete all words after cursor |
Ctrl-u |
delete all characters before cursor |
Ctrl-h / <Backspace> |
delete character before cursor |
<Delete> |
delete character after cursor |
Code runner and REPL
SpaceVim provides an asynchronously code runner plugin. In most language layer,
we have defined a key binding SPC l r for running current buffer.
If you need to add new commands, you can use the bootstrap function. For example:
Use F5 to build project asynchronously.
nnoremap <silent> <F5> :call SpaceVim#plugins#runner#open('make')
These following features have been added to runner and repl plugin:
- Run current file with default command
- Run code file through system file explorer, only supported in gvim.
- Run code per Shebang
- Stop code running
- View output in Output Window
- Set default language to run
- Select language to run
- REPL support
- Run selected code snippet
Highlight current symbol
SpaceVim supports highlighting of the current symbol on demand and add a transient state to easily navigate and rename these symbols.
It is also possible to change the range of the navigation on the fly to:
- buffer
- function
- visible area
To Highlight the current symbol under point press SPC s h.
Navigation between the highlighted symbols can be done with the commands:
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
* |
initiate navigation transient state on current symbol and jump forwards |
# |
initiate navigation transient state on current symbol and jump backwards |
SPC s e |
edit all occurrences of the current symbol |
SPC s h |
highlight the current symbol and all its occurrence within the current range |
SPC s H |
go to the last searched occurrence of the last highlighted symbol |
In highlight symbol transient state:
| Key Bindings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
e |
edit occurrences (*) |
n |
go to next occurrence |
N / p |
go to previous occurrence |
b |
search occurrence in all buffers |
/ |
search occurrence in whole project |
<Tab> |
toggle highlight current occurrence |
r |
change range (function, display area, whole buffer) |
R |
go to home occurrence (reset position to starting occurrence) |
| Any other key | leave the navigation transient state |
Errors handling
SpaceVim uses neomake to give error feedback on the fly. The checks are only performed at save time by default.
Errors management mappings (start with e):
| Mappings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
SPC t s |
toggle syntax checker |
SPC e c |
clear all errors |
SPC e h |
describe a syntax checker |
SPC e l |
toggle the display of the list of errors/warnings |
SPC e n |
go to the next error |
SPC e p |
go to the previous error |
SPC e v |
verify syntax checker setup (useful to debug 3rd party tools configuration) |
SPC e . |
error transient state |
The next/previous error mappings and the error transient state can be used to browse errors from syntax checkers as well as errors from location list buffers, and indeed anything that supports Vim's location list. This includes for example search results that have been saved to a location list buffer.
Custom sign symbol:
| Symbol | Descriptions | Custom options |
|---|---|---|
✖ |
Error | error_symbol |
➤ |
warning | warning_symbol |
ⓘ |
Info | info_symbol |
quickfix list movement:
| Mappings | Descriptions |
|---|---|
<Leader> q l |
Open quickfix list windows |
<Leader> q c |
clear quickfix list |
<Leader> q n |
jump to next item in quickfix list |
<Leader> q p |
jump to previous item in quickfix list |
EditorConfig
SpaceVim has supported EditorConfig, a configuration file to “define and maintain consistent coding styles between different editors and IDEs.”
To customize your editorconfig experience, read the editorconfig-vim package’s documentation.
Vim Server
SpaceVim starts a server at launch. This server is killed whenever you close your Vim windows.
Connecting to the Vim server
If you are using Neovim, you need to install neovim-remote, then add this to your bashrc.
export PATH=$PATH:$HOME/.SpaceVim/bin
Use svc to open a file in the existing Vim server, or use nsvc to open a file in the existing Neovim server.
Achievements
issues
| Achievements | Account |
|---|---|
| 100th issue(issue) | BenBergman |
| 1000th issue(PR) | sei40kr |
| 2000th issue(PR) | nikolaussucher |
| 3000th issue(PR) | nahuef |
Stars, forks and watchers
| Achievements | Account |
|---|---|
| First stargazers | monkeydterry |
| 100th stargazers | robertofarrell |
| 1000th stargazers | mohebifar |
| 2000th stargazers | myakove |
| 3000th stargazers | adrian-spataru |
| 4000th stargazers | seungdols |
| 5000th stargazers | shiningdracon |
| 6000th stargazers | SummerMagic |
| 7000th stargazers | Murderlon |
| 8000th stargazers | dbdr |
| 9000th stargazers | Ruyka |
| 10000th stargazers | royge |